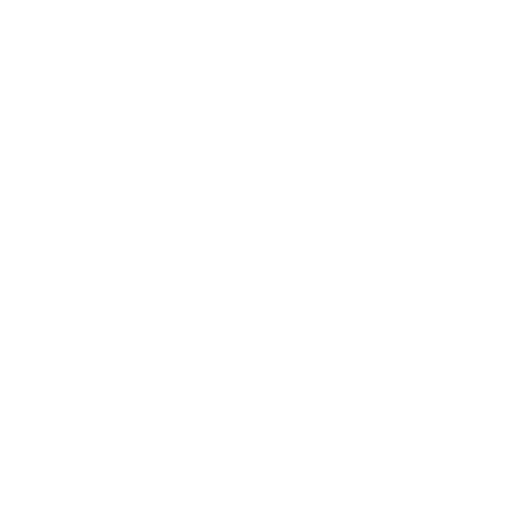
The epididymis is an important organ in the male reproductive system that is responsible for the maturation and transportation of sperm from the testicles to the vas deferens.
This is where the sperm gets matured and are exposed to various fluids that aid with their motility. This article gives a detailed description of what epididymis is and its significance in male fertility.
Significance of Epididymis in Male Fertility
The epididymis plays a crucial role in male fertility. It is a long, coiled tube that sits atop the testicle and is responsible for several key functions that are vital for sperm maturation and transport. Here are the significant aspects of the epididymis in relation to male fertility
Sperm Maturation
Storage: The epididymis serves as a storage site for sperm after they are produced in the testes. It provides an environment for the sperm to mature over several days.
Maturation Process: During their stay in the epididymis, sperm undergo important changes. They acquire motility and the ability to fertilize an egg. This maturation process is essential for the sperm to become fully functional.
Transport of Sperm
Conduits for Movement: The epididymis acts as a conduit through which sperm pass from the testes to the vas deferens and eventually to the outside of the body during ejaculation.
Peristaltic Movement: The smooth muscle in the epididymis walls helps in the peristaltic movement, facilitating the transport of sperm.
Protection and Nourishment
Nutrient Supply: The epididymis provides an environment rich in nutrients that are essential for maintaining the viability of sperm.
Protective Environment: It offers a protective environment against damage and prepares the sperm to withstand the acidic environment of the vagina.
Sperm Quality Control
Removal of Defective Sperm: The epididymis plays a role in removing defective sperm cells, ensuring that only the most viable and healthy sperm are stored and eventually ejaculated.
DNA Integrity: It contributes to the maintenance of DNA integrity in sperm cells, which is crucial for successful fertilization and normal embryo development.
Concentration of Sperm
Concentration for Ejaculation: By the time sperm reach the end of the epididymis, they are concentrated and ready for ejaculation. This concentration is important for increasing the chances of successful fertilization.
What Is Epididymis?
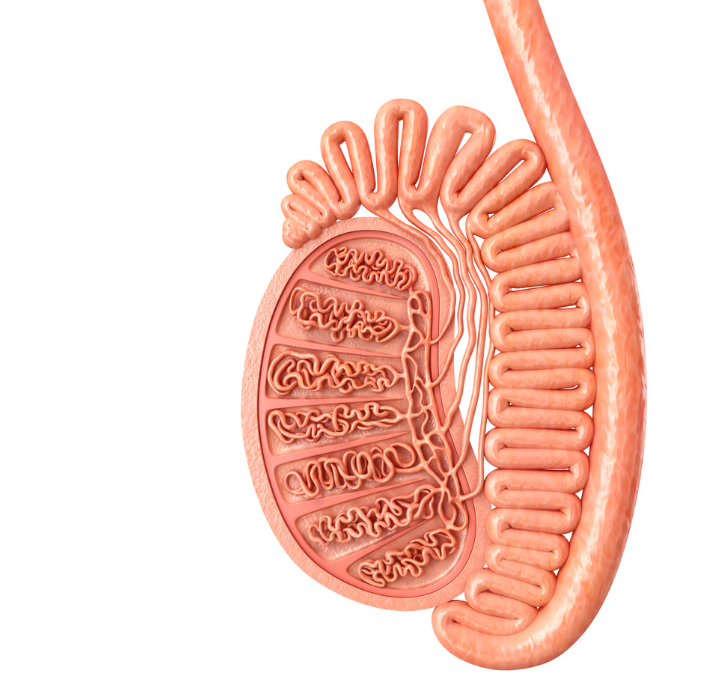
An epididymis is a narrow, tightly-coiled tube in the male reproductive system. It is present inside the scrotum behind each testicle and connects them to the vas deferens. This is where the sperm are stored and reach the final stage of maturation after they are produced in the seminal vesicles.
The epididymis is directly connected to the ejaculatory duct by the vas deferens. The mature sperm are moved to the vas deferens and into the pelvic cavity due to ejaculatory contractions. They are then combined with the semen in the ejaculatory duct and ejected through the urethra during orgasm.
If the sperm are not ejaculated for a longer period, or if vasectomy is performed on the male, the sperm are eventually reabsorbed by the epididymis.
The Epididymis: An Essential Reproductive Organ
The epididymis is one of the most important male reproductive organs that is responsible for the storing and maturation of sperm. The epididymis also includes
- The seminiferous tubules,
- Rete testis,
- Efferent ducts,
- Vas deferens,
- Ejaculatory duct, and
- Urethra.
During the sperm’s journey through the epididymis, it matures and gains the ability to swim. The epididymis plays an important role in the maturation and transport of sperm from the testicles to the vas deferens. Thus, any structural and functional issues with this organ can cause infertility in men.
Epididymal Structure

The epididymis is a convoluted, crescent-shaped organ present in all reptiles, birds, and mammals. It is about 3.8 cm long in humans and is divided into three main anatomical regions: the head (caput), the body (corpus), and the tail (cauda).
- The head (Latin: caput)
The head is the largest part of the epididymis and is attached to the top surface of the testes. It receives sperm cells from the efferent ducts of the testicles. It is characterised by a thick epithelium with long stereocilia and a little smooth muscle.
The concentration of the sperm here is dilute. Thus, the head is responsible for absorbing fluids to make them more concentrated.
- The body (Latin: corpus)
As the sperm travels from the head to the body, the thickness of the muscle wall reduces, and more fluids are absorbed. The sperm starts to become more concentrated.
- The tail (Latin: cauda)
The tail is the smallest and longest part of the epididymis. After the sperm are concentrated and matured in the head and body parts, they are stored in the tail region of the epididymis.
A two-layered pseudostratified epithelium covers the epididymis. There are six types of cells present in the epithelium. They are
- Principal cells
- Basal cells
- Apical cells
- Clear cells
- Intraepithelial lymphocytes, and
- Intraepithelial macrophages.
What are the Functions of the Epididymis?
Epididymis plays a major role in various roles regarding the maturation and transportation of sperm. Below are some of the major functions of the epididymis.
Sperm Transport
This is the first and foremost function of the epididymis. Since the organ connects the testes and the vas deferens, it is responsible for transporting sperm from the testicles to the vas deferens.
The epididymis is approximately 6-7 meters (20-23 ft) long. It may take the sperm up 4 to 6 weeks days to travel through the epididymis and become a fully mature and motile sperm.
Sperm Concentration

The epididymis is where sperm reaches maturity and gains other functions. This process occurs in the head and body parts of the epididymis, where they absorb fluids that make the sperm more concentrated.
Increased sperm concentration of sperm is essential for sperm to be more concentrated in the semen. This is an important factor that can affect male fertility.
Sperm Protection

The epididymis is also responsible for the protection of sperm from the external environment. It excretes various antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase into the epididymal lumen to neutralise the reactive oxygen generated by the metabolic activity of the epithelial cells.
It also has a blood-epididymis barrier to shield the maturing sperm from the immune system and other harmful substances in the bloodstream.
Sperm Storage

The tail (cauda) region of the epididymis is responsible for storing the mature sperm before ejaculation. At a given period, about 50-80% of the sperm are stored in the tail of the epididymis.
The epithelial cells present in the tail secrete factors that keep the environment luminal and maintain the sperm in an inactive state during storage. After ejaculation, sperm wake up from their quiescent state and regains motility. Their metabolic activity also increases by 3 to 5 times compared to when they were in the cauda epididymis (tail).
Sperm Maturation

Sperm maturation is an essential part of male fertility. Only a mature sperm can fertilise an egg in natural conditions.
During the time that the sperm travel through the epididymis, it undergoes various maturation changes. The fluid absorbed by the epididymis’s head (caput) and body (corpus) makes the sperm more concentrated and aids their maturation. They also undergo changes and acquire motility and other functions necessary for successful fertilisation
Acquisition of Motility

The immature sperm produced by the testicles are immobile. As the sperm travels through the epididymis and finally reaches the tail (cauda) region, they mature and are capable of progressive motility.
Sperm can also mature and attain motility in artificial conditions. However, the epididymal lumen provides the best environment for the sperm to attain mobility. Sperm undergoes several morphological and structural changes to become motile and gain the ability to swim.
Fertilisation Capabilities
In addition to aiding sperm with maturation, epididymis also provides the sperm with the necessary factors for fertilisation. They acquire factors necessary to bind and penetrate the cumulus cells and zona pellucida.
The carbohydrate-protein interactions between the oligosaccharides on the oocyte (egg) membrane and the receptor proteins on the sperm membrane is the primary mechanism responsible for sperm-oocyte binding.
Sperm Maturation and Reproduction

It is a proven fact that proper maturation of the sperm is important for successful fertilisation and reproduction. Sperm that are not fully matured can have adverse effects on the reproductive potential and early embryogenesis.
Epididymis and male fertility
From the above article, it is clear that epididymis plays an important role in male fertility and the fertilization of oocytes. Only when the sperm are successfully matured and has good mobility can they swim through the uterus to reach the eggs in the fallopian tubes. Issues in Epididymis or any other Fertility issues must need an immediate attention. So, it is best get a consultation from a Fertility doctor if you undergone any fertility issues.
Frequently asked questions
That sperm takes about 4 to 6 weeks to travel through the epididymis until it reaches the tail (cauda) of the epididymis. During this time, the sperm reaches maturity and attains motility along with other factors necessary for successful fertilisation.
The primary functions of the epididymis are sperm maturation and transport. Epididymis is present in several species. As the sperm travel through the epididymis, they are exposed to fluids that make them more concentrated and mature.
Epididymitis is the inflammation of the epididymis and can cause intense pain in the testicles. It can occur in males of any age, but it is more common in men between the ages of 14 and 35.
Chronic epididymitis can affect sperm count and motility. It can cause sperm to not be mature enough for fertilisation of oocytes. In addition, it can affect sperm motility, resulting in atypical staining of sperm tails.