Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) is getting quite common nowadays, and almost one in five women is affected by it globally. PCOS is the condition of hormonal imbalances in the body that will lead to difficulty getting pregnant or complications during pregnancy.
PCOS doesn’t always lead to infertility. Women can get pregnant despite having PCOS, but the chances of getting pregnant decrease by about 70%
Women can undergo fertility treatments to tackle PCOS and get pregnant. This article discusses what PCOS is and how they impact a woman’s fertility.
How PCOS impacts fertility
PCOS is one of the most common causes of anovulatory infertility (infertility caused due to lack of ovulation). Most women who are diagnosed with anovulatory infertility have PCOS. They only learn that they have PCOS when they are visiting a hospital for infertility treatments.
Women with PCOS experience an increase in the Luteinizing Hormone (LH) and a decrease in the Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH). This, combined with the effects of increased androgen and insulin secretion, can cause infrequent or lack of menstruation.
This can impact their pregnancy level and make it difficult for them to conceive a child. Women with PCOS who conceive are at a higher risk of developing gestational diabetes or suffering from spontaneous abortion in the first trimester (loss of pregnancy before twenty weeks of gestation).
Symptoms of PCOS
Below are some of the most common symptoms of PCOS.
- Irregular periods: The most common cause of PCOS, women with PCOS may have missing periods or no periods at all. They may also experience heavy bleeding during periods.
- Cysts: Women with PCOS have enlarged cysts in the ovaries. They can be found through ultrasound scans.
- Infertility: Irregular periods and hormonal imbalances can cause infertility in women.
- Obesity: Almost 40-80% of women with PCOS suffer from obesity and have trouble maintaining a healthy weight.
- Abnormal hair growth: The excess secretion of androgen may cause hair growth in the facial, arms, chest, and abdominal areas (Hirsutism). Almost 70% of women with PCOS suffer from this.
- Acne: PCOS can cause acne to develop in the face, back, and chest areas. This is a bit difficult to treat and may last longer.
- Dark patches on the skin: Women may develop dark patches on the neck folds, armpits, groin (between the legs), and under their breasts. This condition is called acanthosis nigricans.
- Thinning hair: Women with PCOS can experience increased hair fall and start having bald patches on the head.
Note It is possible for some women with PCOS not to experience any of the above symptoms. They won’t even realize they have PCOS until they start gaining weight suddenly or have issues getting pregnant. It is also possible to have mild PCOS, where the symptoms aren’t too severe and are barely noticeable. |
What is Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)?
PCOS is becoming quite common nowadays. It is a medical condition where the ovaries don’t release an egg every other month at the end of the menstrual cycle. This can lead to irregular periods and infertility.
The irregular periods women suffer may be either not having periods every other month or having periods that may last many days. Some women may also have too much androgen (male hormone) in their bodies.
Women with PCOS have numerous small cysts (fluid-filled sacs) in their ovaries. These cysts contain immature eggs that were not released by the ovaries. These cysts release androgen in high amounts and disrupt the flow of the menstrual cycle.
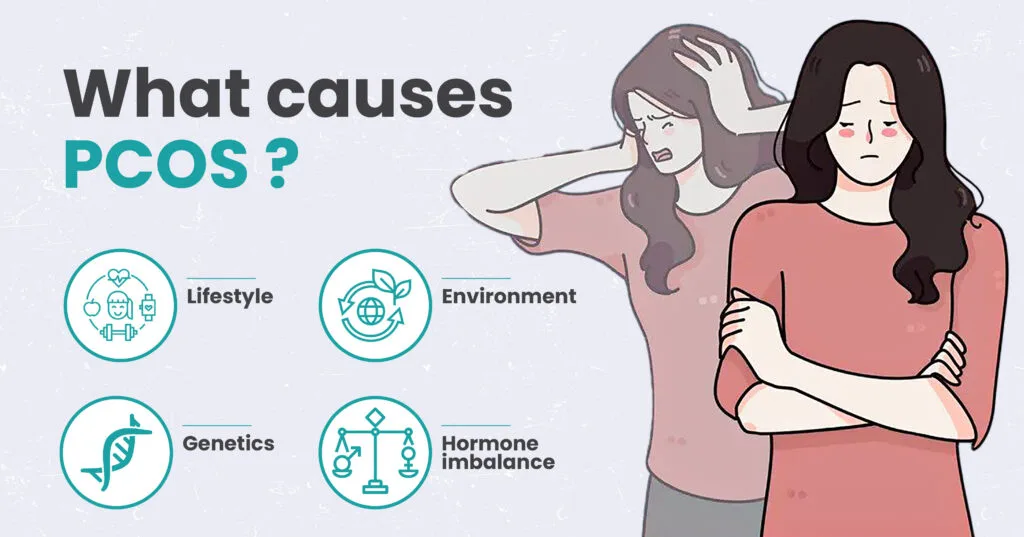
What are the causes of PCOS?
The exact cause of PCOS is unknown. It may be genetic or may be caused due to the changes in the lifestyle and food habits of women. Most times, PCOS is caused due to the secretion of an excess amount of androgens.
Both male and female bodies produce the hormones estrogen and androgen. The female body produces more estrogen (female hormone) and less androgen (male hormone), and vice versa. PCOS occurs when the female body produces more androgen and less estrogen.
This disrupts the body from carrying out basic female functions like the menstrual cycle and causes infertility.
The other cause of PCOS is insulin resistance. The insulin secreted by the pancreas allows body cells to use sugar(glucose) as the primary energy source. If the body becomes resistant to this process, the sugar level in the body will increase.
The body will release more insulin to take down the sugar levels. Too much insulin in the body releases androgen, which can affect ovulation and cause PCOS.
Fertility treatments for women with PCOS
Currently, there are no definitive treatments for PCOS. Doctors suggest treatments or medication based on the goal of the treatment. Most treatment plans for PCOS deal with resolving issues with ovulation and tackling metabolic issues like insulin resistance.
Doctors will first suggest some non-medical remedies like reducing weight, following a healthy diet plan, and tracking periods to understand the ovulation cycle. If these methods don’t work, there are some treatments and medications that can be followed to treat PCOS.
Clomiphene citrate (Clomid)
Clomiphene citrate is an oral medication that can stimulate ovulation in the body. This medicine works by stimulating the production of FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone). This hormone, in turn, stimulates the ovaries to produce one or more egg follicles.
The dosage and the frequency of the medication is decided by the doctor. Generally, the medicine is taken once a day for 5 days at the beginning of the menstrual cycle.
Letrozole (Femara)
Like Clomid, Letrozole, sold by the name Femara are also pills that can stimulate ovulation. They are usually administered to tackle breast cancer, but they are also effective in jump-starting the ovaries to ovulate.
This medicine should be taken for five consecutive days with the dosage recommended by the doctor. Usually, the recommended dosage lies between 2.5 and 7.5 mg.
Metformin
Metformin is not as effective as the above medicines in curing PCOS. they are primarily used to treat Type 2 Diabetes by boosting the body’s ability to use insulin and lessen blood sugar levels.
Though they can induce ovulation, they are not recommended to women who are trying to get pregnant. So, women who only want to ovulate and not get pregnant can use this medication.
| Metformin can cause some minor side effects like heartburn, stomachache, nausea, etc., when you start taking them. The effects will lessen over time, but it is recommended to consult your doctor before taking this medicine. |
Gonadotropins
Gonadotropins are injections that can help women ovulate. They are the LH and FSH hormones that are usually produced by the pituitary glands. These hormones are responsible for stimulating the ovaries to produce follicles that contain the eggs.
If the LH and FSH are released in low amounts by the body. Gonadotropins can replace them and stimulate ovulation.
Surgery
If none of the above medications worked in inducing ovulation, women can opt for laparoscopic ovarian surgery.
Anovulation is majorly caused due to cysts that thicken the outer layer of the ovaries. This blocks the ovaries from producing eggs. This surgery is done to make small incisions on the ovarian surface to facilitate ovulation.
The results of this treatment are not permanent and can only promote ovulation for 6 to 8 months. They are done under general anesthesia as an outpatient procedure.
PCOS and pregnancy
Having PCOS during pregnancy can lead to a series of complications like
- High blood pressure (hypertension),
- Gestational diabetes,
- Miscarriage, and
- Pre-eclampsia
If you have PCOS, you are also more likely to have a baby that is bigger than expected for its gestational age. This increases the risk of requiring a cesarean section.
Babies born to mothers with PCOS are more likely to be admitted to a neonatal intensive care unit. Pregnant women with PCOS may be more prone to miscarriage or stillbirth.
If you have PCOS and are pregnant, you should consult your Fertility Specialist immediately. These risks can be avoided by closely monitoring your PCOS symptoms and taking extra precautions during your pregnancy.
What are my chances of conceiving with PCOS?
Being diagnosed with PCOS does not mean that women can’t become pregnant. It may just be a little more difficult, and women may want additional assistance. There are many remedies women can follow at home and with medical therapy to manage PCOS symptoms and increase their chances of ha a healthy pregnancy.
Here are some steps women can follow to have a healthy pregnancy despite suffering from PCOS.
- Measuring their Body Mass Index (BMI) and trying to maintain a healthy body weight.
- Starting a healthy diet and exercise plan. Women must stay active and adopt a healthy lifestyle.
- Using an ovulation calendar and tracking their menstrual cycles.
- Checking their body sugar levels. Women should maintain balanced body sugar levels to get pregnant.
Mental Health and PCOS
Finding out about reproductive troubles may be devastating, and emotions like shame and failure are common. However, people should be optimistic and think of it as a medical problem that, like most other ailments, can be treated. This should not be used to judge a woman.
Working through multiple therapies may be a lengthy, stressful, and unpleasant experience for some couples, especially if they have to take time off from an unsupportive workplace. Couples should try to be as supportive of each other as possible during consultations, treatments, and appointments.
Alternative Remedies
Apart from medication and surgery, women can also follow other alternatives that can help treat PCOS and infertility. Though they cannot completely cure infertility, they are a healthy choice for women who don’t want to undergo medical treatments.
Diet and exercise
Maintaining a healthy diet is important for everyone, regardless of age and health conditions. Research proves that a low-calorie diet with fewer carbs and all essential nutrients can improve insulin sensitivity and fertility for women with PCOS.
As for exercise, women can opt to do moderate exercise for about 30 minutes thrice a week to maintain a healthy weight. Overdoing exercise can give the opposite results, so moderate exercise will be fine.
Women suffering from obesity (high BMI) can also do exercises to lose excess weight. They can consult a nutritionist or a fitness coach and get a weight loss plan to follow.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a safe way to treat PCOS in women. Some studies prove that acupuncture works in increasing the blood flow to the ovaries and reducing the number of cysts formed around them.
It also helps manage hyperglycemia, reduces cortisol levels, and assists in weight loss.
Herbs and supplements
Some people prefer to use herbs and other supplements to tackle PCOS. Though the effectiveness of these supplements has not yet been proven, many women use inositol and omega-3 fish oil supplements to treat PCOS. It is better to consult a doctor before taking these supplements.
PCOS and endometriosis
Endometriosis is another major cause of infertility that may or may not be caused due to PCOS. Endometriosis is when the tissue lining the uterus grows in other body parts like
- The outer layer of the uterus,
- The fallopian tubes,
- The ovaries,
- The peritoneum,
- The uterosacral ligaments, and
- Anyplace between the bladder, uterus, and vagina.
While there is usually no association between PCOS and endometriosis, studies found that women with PCOS have a high chance of developing endometriosis. This is caused when the high levels of androgen and insulin in the body indirectly increase the amount of estradiol (an estrogen hormone).
Estradiol is responsible for developing reproductive organs and is the most important hormone during a woman’s reproductive years. It regulates how uterine tissue grows and is closely associated with the development of endometriosis.
Further study proves that women with PCOS whose condition hasn’t improved after infertility treatments are most likely to be affected by endometriosis.
Conclusion
Women with PCOS can get pregnant. They will most likely need to maintain a healthy weight, control their blood sugar levels, and treat other PCOS symptoms with healthy lifestyle changes and medicines.
Sometimes, fertility drugs alone may help them get pregnant. If that fails, they may require assisted reproductive techniques like IVF, IUI, ICSI, etc.
But, no matter what treatment they try, women should not give up hope. There are chances that they can get pregnant sooner than expected with proper care and treatment.
Frequently asked questions
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal condition that affects 5% to 10% of women of reproductive age. Anovulatory infertility (unable to ovulate) is the primary side effect of PCOS, and the prevalence of PCOS is greater in women with anovulatory infertility, ranging from 70% to 80%.
PCOS can cause missing or irregular menstrual cycles. Infertility (inability to conceive) can be caused by irregular menstruation. In fact, PCOS is one of the most prevalent reasons for female infertility.
But, this doesn’t mean that women can’t get pregnant. They can undergo the necessary treatments and treat PCOS-induced infertility.
Below are some of the most common symptoms of PCOS.
- Irregular periods.
- Formation of cysts around the ovaries.
- Infertility.
- Obesity.
- Abnormal hair growth (face, chest, and other areas)
- Acne.
- Dark patches on the skin.
- Thinning hair and baldness on the head.
Female sex hormones, especially estrogen are imbalanced in women with PCOS. The imbalance may prevent mature eggs from developing and releasing from the follicles. Ovulation and pregnancy cannot occur if there are no mature eggs to fertilize.
It’s important to remember that just because a woman has PCOS doesn’t indicate she’s infertile and can’t get pregnant. According to research, 70 to 80% of these women are infertile. This means that up to 30% of women with PCOS have the chance of becoming pregnant on their own without using fertility medications.